Blink
Intravitreal Cysticercosis With Exvaginated Scolex
By Sarakshi Mahajan, MBBS, and Vishali Gupta, MD, Advanced Eye Centre, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
Photo by Arun Kapil, Advanced Eye Centre, PGI Chandigarh, India
Download PDF
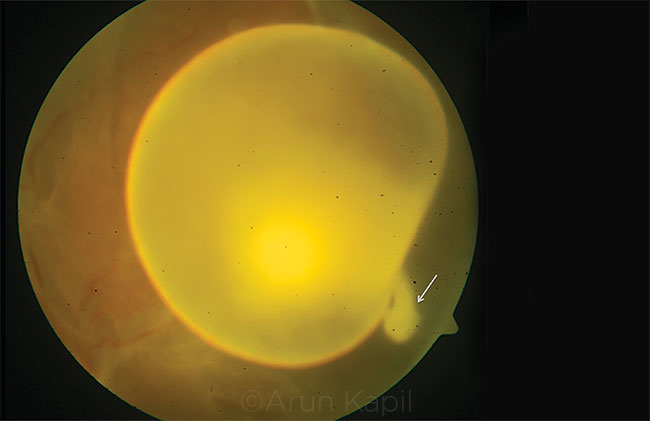
A 26-year-old man presented with complaints of blurred vision in the left eye. His best-corrected visual acuity was 20/400 in the left eye. Funduscopy in the left eye showed a single translucent, freely floating cyst with a dense white spot and undulating movement characteristic of Cysticercus cellulosae. The scolex showed a momentary exvagination from the cyst and was captured photographically. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain did not show any evidence of cysticercosis. The patient underwent pars plana vitrectomy for surgical removal of the cyst.
C. cellulosae, the larval stage of Taenia solium, is a common intraocular parasite that enters the eye from the choroid, lodges under the retina, and may migrate into the vitreous cavity. Typically, the scolex remains invaginated, forming a hyperdense white center. In our patient, the cyst showed an exvaginated scolex.
| BLINK SUBMISSIONS: Send us your ophthalmic image and its explanation in 150-250 words. E-mail to eyenet@aao.org, fax to 415-561-8575, or mail to EyeNet Magazine, 655 Beach Street, San Francisco, CA 94109. Please note that EyeNet reserves the right to edit Blink submissions. |