Corneal Topography
What Is Corneal Topography?
Corneal topography is a special photography technique that maps the surface of the clear, front window of the eye (the cornea). It works much like a 3D (three-dimensional) map of the world, that helps identify features like mountains and valleys. But with a topography scan, a doctor can find distortions in the curvature of the cornea, which is normally smooth. It also helps doctors monitor eye disease and plan for surgery.
What Conditions Is Corneal Topography Used for?
- Scarring. Trauma (injury) or infections can scar the cornea. This changes the shape of the cornea. A topography scan measures the distortion and its effect on vision.
- Growths. The size of pterygia or other growths can be monitored with topography.
- Astigmatism and keratoconus. Topography can help find astigmatism and early cases of keratoconus and track their progression.
- Contact lens fitting. Topography scans help find what type of contact lens can be worn to improve vision. If the scan shows a lot of distortion, sometimes a special hard contact lens (RGP) can help correct vision.
How Does Corneal Topography Help with Surgery?
- Refractive surgery. During refractive surgery like LASIK, the shape of the cornea is changed to correct refractive errors like myopia (nearsightedness). A topography scan helps the surgeon understand how to precisely reshape the cornea.
- Cataracts. When cataracts make the eye’s natural lens cloudy, it is replaced with an intraocular lens (IOL) during cataract surgery. Corneal topography helps surgeons select the right IOL in some cases.
- Corneal transplants. After a corneal transplant, a surgeon may use corneal topography to help a patient heal correctly. The images help assess which stitches should be removed and when based on the shape of the cornea.
- Corneal cross-linking. Corneal cross-linking surgery helps strengthen a cornea with keratoconus. A topography scan may be done to see if this surgery is needed. After surgery, scans are done to monitor the eye.
What to Expect During a Corneal Topography Scan
- You will be seated facing a large bowl with lighted circles inside it. The chin and forehead rests keep your head secure to get the clearest images.
- You will be asked to stare at a fixed target in the bowl while the pictures are taken.
- The scan only takes a few seconds, but it may need to be repeated a few times.
- Getting a corneal topography is painless, as nothing touches your eye during the scan.

Your doctor may look over the images with you during the exam or at a follow-up exam.
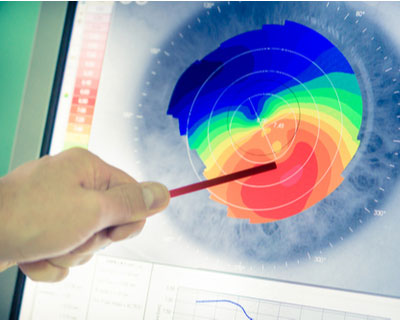
A sample image of what a corneal topography scan might look like.