Download PDF
An international team of researchers has concluded that all patients who present with stage IV uveal melanoma should be evaluated and staged for metastatic disease at initial presentation.1 And because even small intraocular tumors may spread to multiple organs beyond the eye, the researchers recommend whole-body positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT) imaging to avoid missing metastases, which are the leading cause of death due to uveal melanoma.
These conclusions, based on data from an internet-based retrospective registry representing eight countries and 10 oncology centers, were developed by the Ophthalmic Oncology Task Force of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). “Data sharing allowed us to compile significant medical evidence that answereda specific ophthalmic oncology question: What are the clinical characteristics of patients who presented with metastatic uveal melanoma?” said Paul T. Finger, MD, at The New York Eye Cancer Center in New York City.
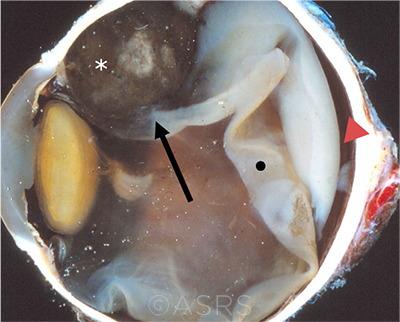 |
CILIARY BODY. This enucleation specimen shows a pigmented, nodular-shaped ciliary body melanoma (arrow) with extensive necrosis (*), a retinal detachment, and subretinal fluid (arrowhead). The retina is folded (•). This image was originally published in the ASRS Retina Image Bank. McGill University Health Center-McGill University Ocular Pathology & Translational Research Laboratory. Ciliary Body Melanoma. Retina Image Bank. 2020; Image Number 55934. © The American Society of Retina Specialists.
|
Data collection. The data analysis, which characterized metastases to determine the amount and spread of disease, included site of origin, tumor thickness, largest basal diameter, extrascleral extension, ciliary body involvement, and the AJCC’s classification system (stages T1-T4).
Findings on stage IV. Of 3,610 patients diagnosed between 2001 and 2011 with uveal melanoma, 69 (1.9%) presented with stage IV disease. Most of the primary tumors in this group of patients originated in the choroid (80%), followed by the ciliary body (16%) and iris (4%).
Significant predictors of metastasis included tumor thickness and largest basal diameter. Most tumors metastasized to the liver (91%), followed by lung (16%), bone (9%), and brain (6%). Multiple sites of metastases were noted in 24% of patients—and, Dr. Finger noted, “PET/CT [imaging] was significantly more likely to reveal multi-organ metastasis.”
Clinical impact. Dr. Finger noted that many centers only perform initial radiographic imaging of the liver—or a chest X-ray and blood testing—prior to treatment. But the results of this analysis suggest that “staging with liver imaging alone risks missing extrahepatic sites of metastasis,” said Dr. Finger, who routinely performs whole-body initial staging on his patients.
Overall, the findings support those of previous studies in suggesting that patients with higher T-category tumors should be more closely monitored for metastatic disease. They also provide a reminder that even small tumors can spread, as 11% of those with metastatic uveal melanoma belonged to the lowest AJCC category (T1).
Finally, in a novel finding, 6% of uveal melanoma patients with metastatic disease belonged to subcategory T1a.
—Miriam Karmel
___________________________
1 Gang G et al. Br J Ophthalmol. Published online Jan. 15, 2021.
___________________________
Relevant financial disclosures—Dr. Finger: Liberty Vision: O.
For full disclosures and the disclosure key, see below.
Full Financial Disclosures
Dr. Abràmoff Alimera: C; Digital Diagnostics: C,O,P; NovaGo: C.
Dr. Finger Liberty Vision: O.
Dr. Foster Aciont: S; Alcon: S,L; Aldeyra: C,S; Allakos: C; Allergan: L; Bausch + Lomb: C,S; Clearside: S; Dompé: S; Eyegate: C,S,O; Genentech: C; Novartis: C,S; pSivida: C,S; Mallinckrodt: S,L.
Dr. Miller Alcon: C; Johnson & Johnson: C,P; Lensar: C; Oculus: C.
Dr. Sun Adaptive Sensory Technology: S; Boston Micromachines: S; Genentech: C; Novartis: C; Novo Nordisk: C,S; Optovue: S; Roche: C,S.
Disclosure Category
|
Code
|
Description
|
| Consultant/Advisor |
C |
Consultant fee, paid advisory boards, or fees for attending a meeting. |
| Employee |
E |
Employed by a commercial company. |
| Speakers bureau |
L |
Lecture fees or honoraria, travel fees or reimbursements when speaking at the invitation of a commercial company. |
| Equity owner |
O |
Equity ownership/stock options in publicly or privately traded firms, excluding mutual funds. |
| Patents/Royalty |
P |
Patents and/or royalties for intellectual property. |
| Grant support |
S |
Grant support or other financial support to the investigator from all sources, including research support from government agencies (e.g., NIH), foundations, device manufacturers, and/or pharmaceutical companies. |
|
More from this month’s News in Review