By Jonathan Hernandez-Siman, MD, and Rona Z. Silkiss, MD, FACS
Edited by Sharon Fekrat, MD, and Ingrid U. Scott, MD, MPH
Download PDF
Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma (NXG) is 1 of 4 adult orbital xanthogranulomatous diseases, along with adult-onset asthma with periocular xanthogranuloma, Erdheim-Chester disease, and adult-onset xanthogranuloma. This group of diseases is characterized histologically by infiltration of foamy histiocytes, Touton-type giant cells, lymphocytes, and varying degrees of fibrosis.1 These disorders may have systemic associations as well as a potentially destructive local course. Patients with xanthogranulomatous disease of the orbit often first seek help from an ophthalmologist. Thus, although these disorders are rare, it is important for the clinician to recognize them, given their potentially serious consequences.
NXG, the focus of this article, is characterized by degeneration of collagen, which is termed necrobiosis.1 It may present as subcutaneous skin lesions that ulcerate or become fibrotic (Fig. 1).2 It is frequently associated with paraproteinemia and multiple myeloma (MM), although other systemic findings may arise. NXG affects adults aged 20 to 85 years, with no significant gender predilection.2
 |
|
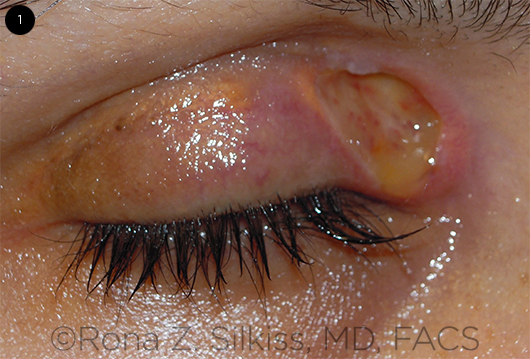
CLINICAL CASE. 38-year-old woman with biopsy-confirmed necrobiotic xanthogranuloma. She presented with right periorbital inflammation and leukopenia; she also had bilateral scleritis that was unresponsive to azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, rituximab, and adalimumab. She eventually developed a yellow periorbital plaque that ulcerated, as seen here. After a long and complicated course, the patient showed improvement on a regimen of low-dose prednisone, cyclophosphamide, thalidomide, and monthly intravenous immunoglobulin infusions.
|
Pathophysiology
The orbital xanthogranulomatous diseases are a type of non-Langerhans histiocytosis with local and/or systemic proliferation of histiocytes.1 Histiocytes are cells derived from circulating monocytes. The latter are produced in the bone marrow and cross vessels to penetrate into tissues, where they mature in either the mononuclear-phagocytic system or the dendritic cell system.
NXG originates from the mononuclear-phagocytic system, which consists of phagocytic monocytes and free and fixed tissue macrophages. The pathogenesis is not completely understood, but it has been postulated to occur secondary to a reactive proliferation of free tissue macrophages.1 Possible causes for this proliferation include induction by a virus, paraproteinemia, immunoglobulin (Ig) or lipid-Ig complex deposition, Borrelia species infection, or chromosomal instability.1,3,4
Pathology
Although there are histologic differences among them, all adult-onset xanthogranulomatous diseases are characterized by infiltration of histiocytes and Touton-type giant cells.1 Xanthoma cells, which often appear as sheets of mononucleated foamy histiocytes, infiltrate the orbicularis muscle and orbital tissue (Fig. 2A). While fibrosis can occur in various disease types, specimens of NXG will exhibit necrobiosis (degeneration of collagen). Lymphocytes, plasma cells, and cholesterol clefts within areas of necrobiosis may be observed1,3,5 (Fig. 2B).
Immunohistochemically, the foamy histiocytes are strongly positive for CD68, CD163, and factor XIIIa, and are usually negative for CD21, CD35, S100, and CD1a.1 Tissue analysis should include testing for the presence of fungal and mycobacterial microorganisms as well as polarizable material to rule out an infectious or foreign body etiology.
 |
|
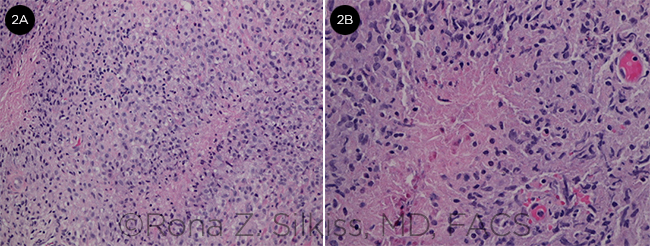
HISTOLOGY. Histologic appearance of a necrobiotic xanthogranuloma removed from a 56-year-old woman. (2A) Images shows xanthoma cells (foamy histiocytes), as well as pink areas of necrobiosis (degeneration of collagen) surrounded by lymphohistiocytic proliferation. (2B) Higher magnification image showing necrobiosis.
|
Systemic Associations
The 4 adult xanthogranulomas have different systemic manifestations.6
NXG is frequently associated with paraproteinemia, usually an IgG monoclonal gammopathy, which is found in up to 80% of cases.1 MM, cryoglobulemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, and other myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative diseases have also been associated with NXG.1,3 Reported rates of associated MM range from 6% to 22%.3 Bone marrow biopsy may reveal atypical or increased plasma cells.3 The mean time from the appearance of NXG lesions to the onset of hematologic disorders is 2.4 years, although hematologic malignancy has been reported from 8 years before to 11 years after skin involvement.1,3,5
Of note, extracutaneous lesions can also develop elsewhere in the body, most commonly in the respiratory tract and heart.3
Adult-onset asthma with periocular xanthogranuloma, while characterized by periocular xanthogranulomas and asthma, also exhibits lymphadenopathy and is often associated with increased IgG levels.
Erdheim-Chester disease is considered the most devastating of the adult-onset xanthogranulomas. It is characterized by fibrosclerosis of the orbit and the internal organs, which can lead to vision loss and death.
Adult-onset xanthogranuloma is an isolated xanthogranuloma without systemic involvement.
NXG Signs and Symptoms
NXG presents with subcutaneous skin lesions that tend to ulcerate and become fibrotic. The most common site of involvement is the periorbital region (>80% of cases); however, the face, trunk, and extremities can also be affected.4 Skin lesions may be indurated papules, nodules, or plaques that can be violaceous, red-orange, or yellow (xanthomatous) in color.1 Lesions are often asymptomatic but can be pruritic.3 Papules often enlarge and can scar, ulcerate, atrophy, or form telangiectasias.3 Ulcerations are seen in more than 40% of patients and can be striking (see Fig. 1).1 The size of the plaques varies widely, from 0.3 cm to 25 cm.1
Periorbital lesions may be unilateral or bilateral, involve one or more eyelids, and cause blepharoptosis.1,3 Locally, the indurated and ulcerated lesions can disrupt adjacent ocular structures. If there is deeper extension of the lesions into the orbit, patients may report blurred vision, diplopia, or transient vision loss and may develop proptosis, strabismus, scleritis, keratitis, iritis, and conjunctivitis.1,3,4
Since the first description of the disease in 1980, NXG has been associated with an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate.3 Other associated lab abnormalities include leukopenia, C4 deficiency, and elevated cholesterol level.3 Radiologic studies of the orbit may reveal evidence of proptosis, an abnormal infiltrative soft tissue mass, increased intraorbital fat, enlargement of extraocular muscles, and possible lacrimal gland involvement (Fig. 3).1,3
 |
|
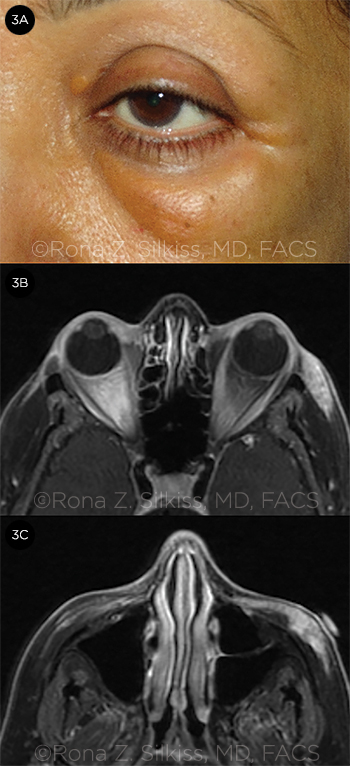
VIEWS OF NXG. (3A) Clinical appearance of a 56-year-old woman with biopsy-confirmed NXG, and (3B, 3C) MRI views of her orbits. T1 images with gadolinium show left-sided thickening of the orbicularis oculi muscle with heterogeneous contrast enhancement.
|
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of adult xanthogranuloma is made by histopathology. The histologic features of the specimen, along with the systemic manifestations experienced by the patient, are the basis for distinguishing among the 4 types of adult orbital xanthogranulomatous disease described above.
Differential diagnosis. In addition to the other 3 adult-onset orbital xanthogranulomas, the differential diagnosis for NXG includes foreign body granuloma, xanthogranulomatous inflammation due to infection, xanthoma, Langerhans cell or other form of histiocytosis, sarcoidosis, granular cell tumor, necrobiosis lipoidica, amyloidosis, subcutaneous rheumatoid nodule, granuloma annulare, lymphoma, nonspecific orbital inflammation, and epithelioid sarcoma.
NXG Treatment
Patients diagnosed with NXG should be referred to a hematologist-oncologist for a workup (potentially including serum protein immunoelectrophoresis, flow cytometry, and/or bone marrow biopsy). Lifelong surveillance for associated malignancy is required.5 Ulcerated lesions should be managed with cleansing and antibiotic ointment.
Attempts to treat this rare disorder have been varied and often unsuccessful.3,7 Medical treatments that have shown favorable results include intralesional and systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressive therapy with biologics (e.g., rituximab) or alkylating agents (e.g., chlorambucil) either alone or in conjunction with steroid treatment, and radiation therapy.3,6 Surgical debulking may be considered; however, 42% of patients in 1 study had recurrence after surgical intervention, leading the authors to advocate for deferral of surgical debulking for as long as possible.4,5 We favor tailoring the treatment decision to the patient, taking into account factors such as an underlying hematologic condition and the extent of disruption to orbital structures or the globe.
Prognosis
The disease is usually chronic and slowly progressive and shows a variable response to therapeutic agents.3 As discussed above, patients with NXG require lifelong monitoring for hematologic malignancy, which may appear years after skin lesions.1,3,5 A 90% survival rate at 15 years has been reported for patients with NXG.5
___________________________
1 Kerstetter J, Wang J. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33(3):457-463.
2 Guo J, Wang J. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133(12):1994-1997.
3 Spicknall KE, Mehregan DA. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48(1):1-10.
4 Balagula Y et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(11):e305-307.
5 Ugurlu S et al. Am J Ophthalmol. 2000;129(5):651-657.
6 Sivak-Callcott JA et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;90(5):602-608.
7 Miguel D et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. Published online July 19, 2016. doi:10.1111/jdv.13786.
___________________________
Dr. Hernandez is an ophthalmology resident, and Dr. Silkiss is the Chief of Oculoplastics; both are at California Pacific Medical Center, San Francisco. Relevant financial disclosures: None.