By Guneet S. Sodhi, MD, John D. Sheppard, MD, and Rohit S. Adyanthaya, MD
Edited By: Ahmad A. Aref, MD, MBA
Download PDF
Jessica Taylor,* an otherwise healthy 11-year-old girl, had started experiencing blurred vision in her right eye, as well as a shadow over the top of her right field of vision. After two months, her parents took her to see an optometrist who stated that there was retinal inflammation in Jessica’s right eye and referred her to us.
We Get a Look
When we first saw Jessica, she didn’t mention the shadow, but she may have been nervous and hesitant to say much. She did tell us that there hadn’t been any curtains over her vision and that she hadn’t noticed any floaters or flashes of light.
While talking with Jessica and her parents, we learned that they are avid meat-eaters and, on occasion, eat medium-rare venison. Jessica also told us that she loves to spend time playing with their five cats.
On exam, her vision was 20/40 in her right eye and 20/20 in the left.
In her right eye, she had no anterior segment keratic precipitates (KPs) but did have 1+ vitreous cells and haze. Also in her right eye, the fundus examination (Fig. 1) showed a yellow chorioretinal lesion inferior to the fovea. Of note, there were no chorioretinal scars and no evidence of previous inflammation in either eye.
Visual field testing revealed a large central scotoma in her right eye.
An OCT image (Fig. 2) through the inferior macular lesion demonstrated a large hyperreflective intraretinal lesion corresponding to an area of retinochoroiditis and significant choroidal thickening that was seen on the exam. There were also multiple hyperreflective spots in the vitreous consistent with vitritis.
Our initial differential. Clinically, the focal yellow retinal lesion with associated vitritis immediately pointed toward an infectious or inflammatory etiology, with toxoplasmosis high on the differential. This was supported by Jessica’s history of close contact with cats and eating undercooked meat.
We considered white dot syndromes, trauma, and malignancy to be lower on the differential, based on Jessica’s presentation and history.
What we did. We started Jessica on topical steroids and ordered uveitis labs, which included a complete blood count (CBC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), toxoplasmosis IgM and IgG, syphilis labs (rapid plasma reagin [RPR] and FTA-Abs), TB Quantiferon Gold, and a chest x-ray.
The toxoplasmosis IgG titer was 221 IU/mL (reference range, 0-7 IU/mL), but the IgM antibodies were within normal limits. All the other labs were unremarkable. We referred her to a pediatric infectious disease specialist who started her on oral pyrimethamine 25 mg (daily), oral sulfadiazine 2 g (twice a day), and leucovorin 15 mg (daily), followed by oral prednisone 40 mg (daily) three days after initiating anti-toxoplasmosis therapy.
The next visit. When we saw Jessica a few days later, her retinal exam and vitritis had improved.
Allergic reaction. However, she had developed an allergic reaction to the sulfadiazine (fever, rash, and headaches) and, three days later, to pyrimethamine (rash). Because of her reaction to the sulfadiazine, she was admitted as an inpatient. Both sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine were discontinued. She was started on azithromycin 250 mg (twice a day) and oral clindamycin 150 mg (four times a day) and continued on the oral steroid course.
Vision worsens. Two weeks after starting on azithromycin and clindamycin, a fundus exam and OCT imaging (see “A Second Look at Her Right Eye”) showed improvement in the retinochoroiditis and vitritis. However, after finishing a three-week course of clindamycin, a one-month course of azithromycin, and an oral prednisone taper, Jessica’s vision worsened to 20/50 in the right eye. Furthermore, OCT imaging (Fig. 3) showed increasing hyperreflectivity in the subretinal space.
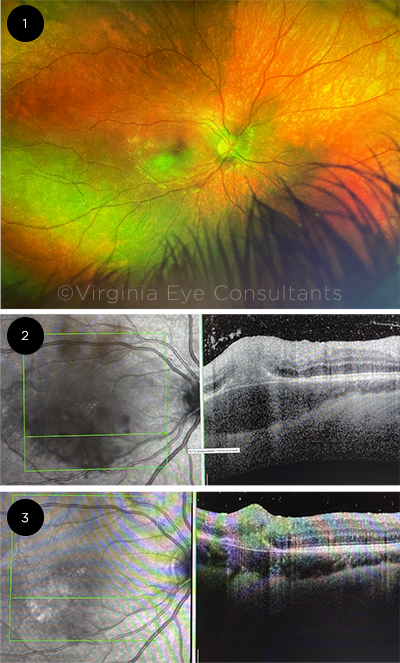 |
|
FIRST WEEKS OF TREATMENT. When we first saw Jessica, (1) a fundus photo of the right eye showed that a yellow cream–colored chorioretinal lesion was present inferotemporal to the macula with overlying vitreous haze. On the same day, (2) an OCT scan through that lesion showed that a large sub-RPE and intraretinal hyperreflective lesion was present with associated choroidal thickening. Multiple hyperreflective spots were present within the vitreous, indicating vitritis. At a later exam, we saw improvement in the retinochoroiditis and vitritis (to see images from that exam, view this article online). However, several weeks after the initial presentation, (3) OCT imaging revealed a new finding of subretinal fluid and a hyperreflective lesion in the subretinal space.
|
The Mystery Fluid
We restarted Jessica on oral clindamycin (three times a day), oral azithromycin, oral prednisone, and topical steroids.
No improvement in vision. One week later, we saw no improvement in her vision or macular subretinal fluid. As we were under the impression that this was an active toxoplasmosis infection refractory to the current regimen, she was given an intravitreal injection of clindamycin in her right eye. She was remarkably cooperative for an 11-year-old. However, her subretinal fluid not only persisted but also increased by the time we saw her the next week. Despite a reduction in the choroidal thickening and vitritis at this visit, the volume of retinal fluid continued to increase. She was started on atovaquone therapy in addition to the other medications.
Pinning it down. A few days later, OCT angiography (OCTA; Fig. 4) showed a definitive secondary choroidal neovascular membrane (CNVM). This, along with a hemorrhage on fundus exam (Fig. 5), clinched the diagnosis.
The CNVM diagnosis was supported by the fact that the vitritis and choroidal thickening were actually improving, indicating that the systemic therapy was adequately treating the infection. Jessica received intravitreal aflibercept (Eylea) as an off-label indication and experienced complete resolution of the subretinal fluid (for an OCT image, see “We Try Aflibercept”). Her final visual acuity was 20/20 in the right eye.
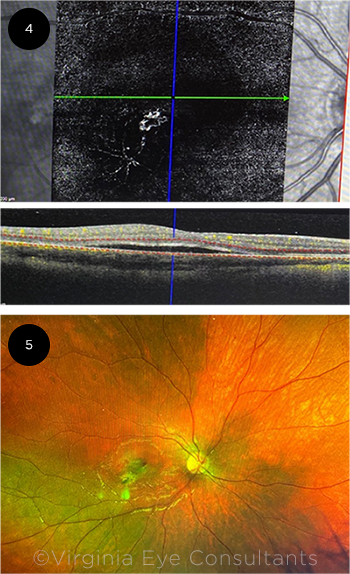 |
|
PINNING DOWN THE DIAGNOSIS. After a further change in medications, (4) OCTA through the area of subretinal fluid showed an obvious neovascular membrane. (5) The fundus exam of the right eye revealed a new hemorrhage in the temporal parafovea, adjacent to the retinochoroidal lesion.
|
Our Diagnosis
With the combination of a positive toxoplasmosis titer, pertinent clinical history, posterior segment inflammation that was responding to fourth-line antitoxoplasmosis therapy, and no prior evidence of chorioretinal scarring, we diagnosed primary ocular toxoplasmosis in an adolescent patient. Jessica presented with only macular involvement, complicated by a CNVM, which is rare in the literature.
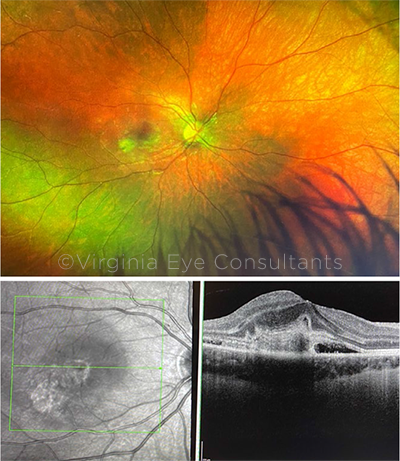 |
|
A SECOND LOOK AT HER RIGHT EYE. Three weeks after the initial presentation, we noted (top image) an interval decrease in the size of the chorioretinal lesion and improved vitreous haze, and (bottom image) the OCT scan showed that the retinochoroidal lesion and overlying vitreous cell was improving.
|
Discussion
Ocular toxoplasmosis is a progressive and recurring necrotizing retinitis caused by infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a ubiquitous obligate intracellular parasite.
Can be congenital or acquired. During a congenital infection, the fetus is infected via the placental bloodstream. During an acquired infection, parasite transfer is typically mediated through the gastrointestinal tract. The main routes of acquired infection are thought to be from ingestion of oocysts from cat feces in soil (via, for example, hand-to-mouth transmission), unwashed fruits and vegetables, and raw or undercooked meat.
A clinical diagnosis. T. gondii is prevalent in nature, and the presence of antibodies to T. gondii is useful only to confirm previous exposures to the parasite. Absence of IgG titers virtually rules out the infection. The combination of high titers of toxoplasmosis IgG and IgM antibodies is usually consistent with recent infection.
Nonetheless, the diagnosis is usually made clinically.1
Impacts the retina and choroid. Once the parasites reach the eye, they will create a focus of retinal inflammation, involving the choroid secondarily. Immune responses of the host induce conversion of the parasitic forms, the tachyzoites, into the dormant bradyzoites and cyst forms, which remain inactive in scars. A reactivation of retinitis from rupture of the cysts can develop near the preexisting scars.
Clinically, the focal necrotizing retinitis is associated with vitritis and, often, with an anterior uveitis, either granulomatous or nongranulomatous. Vitritis is usually intense near the lesion of active chorioretinitis, creating the classic “headlight in the fog” presentation.1
Management. Since ocular toxoplasmosis is a self-limiting disease, some clinicians will not treat small peripheral lesions. However, if treatment is warranted, numerous therapies have been used, with no consensus as to the most efficacious regimen.
The classic treatment regimen consists of triple therapy: oral pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and prednisone, with folinic acid usually added to prevent the leukopenia and thrombocytopenia associated with pyrimethamine therapy. Some clinicians add oral clindamycin as quadruple therapy.
Clindamycin, either alone or in combination with other agents, has been shown to be effective in managing acute lesions and can be used in patients who experience sulfa allergies. This was demonstrated in our patient who had allergic reactions to both sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine.
For patients who do not have sulfa allergies, some physicians prefer trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole due to its low cost and the frequent unavailability of sulfadiazine in pharmacies and potential cost issues with pyrimethamine. For lesions threatening the macula, intravitreal clindamycin has also been suggested, as it bypasses blood-ocular barriers.
Other agents that have been used include doxycycline, minocycline, and atovaquone.2
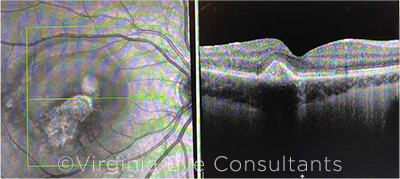 |
|
WE TRY AFLIBERCEPT. After one aflibercept injection, there was significant reduction in the size of the CNVM (indicated by decreased size of the subretinal hyperreflective lesion). The subretinal fluid resolved completely.
|
A Twist in the Story
CNVM rarely complicates toxoplasmic chorioretinitis. A few cases in the literature report this finding, which has been managed with observation, anti-VEGF therapy, antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory medications, laser photocoagulation, or photodynamic therapy, all with variable outcomes.
Increased expression of VEGF and Bruch membrane compromise secondary to inflammation from T. gondii has been posited to contribute to neovascular disease in ocular toxoplasmosis and provides a rationale for intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy.
Furthermore, intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy minimizes the destruction of the retina and choroid and provides a favorable visual outcome.3 Therefore, a number of cases of macular CNVM secondary to ocular toxoplasmosis have improved with anti-VEGF therapy.3-5 With the exception of one case, all of these patients presented with a macular CNVM near a healed, inactive lesion after having had a primary episode of toxoplasmosis. Only one case presented with a macular CNVM at the time of primary acquired Toxoplasma retinochoroiditis.6 Our case is unique to the aforementioned case because Jessica presented with a primary toxoplasmosis lesion without a CNVM and then later developed a CNVM, possibly as an indicator of a poor response to first- and second-line antitoxoplasmosis therapy due to a sulfa and pyrimethamine allergy. This underscores the fact that macular toxoplasmosis should be followed particularly carefully for the development of choroidal neovascularization, especially in younger patients as hypothesized in an analysis by Cotliar and Friedman.7
Last, our pediatric patient only required one intravitreal injection of aflibercept, supporting other studies that hypothesize toxoplasmosis macular CNVMs are exquisitely sensitive to anti-VEGF therapy, particularly in the pediatric population. This reduced number of treatments to achieve involution of CNVMs may be explained by the relative good health of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) pump in younger patients, compared with the RPE pump in adults with age-related macular degeneration. Given that the adverse ocular and systemic side effects of anti-VEGF therapy in children have not been as extensively studied as in adults, a reduced number of intravitreal anti-VEGF agents administered as needed in pediatric patients is strongly advised.5
Long-term studies will be required to establish the safety of these injections in this age group.
___________________________
* Patient name is fictitious.
___________________________
1 Park YH, Nam HW. Korean J Parasitol. 2013;51(4):393-399.
2 Stanford MR et al. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(5):926-932.
3 Benevento JD et al. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126(8):1152-1156.
4 Kohly RP et al. Can J Ophthalmol. 2011;46(1):46-50.
5 Mathur G et al. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2014;7(3):141-143.
6 Mushtaq F et al. Cureus. 2019;11(2):400.
7 Cotliar AM, Friedman AH. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982;66(8):524-529.
___________________________
Dr. Sodhi has just completed an ophthalmic oncology fellowship at the Cleveland Clinic’s Cole Eye Institute and starts a vitreoretinal surgery fellowship at VitreoRetinal Surgery (VRS), based in the Minneapolis region, this month. Dr. Adyanthaya is a vitreoretinal surgeon and assistant professor of ophthalmology, and Dr. Sheppard is a cornea and uveitis specialist and assistant professor of ophthalmology; both are at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, Virginia. Financial disclosures: None.
Further Retina-Related Cases
Tackle these retina-related Morning Rounds cases from the EyeNet archives:
A Teen With Nyctalopia. The 15-year-old, with a history of cystic fibrosis, had been experiencing progressive decreased vision and difficulty with night vision for three years.
The Case of Retinal Spots With Blurred Vision. This 75-year-old was referred with a diagnosis of presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome.
A Mysterious Amelanotic Fundus Mass. The 38-year-old with a freckle at the back of her left eye.
The Black Spot. At first, the overworked 34-year-old ignored the black spot in his vision. But over three weeks, it grew in size and the letters on his computer screen began to blur.
|