Download PDF
Despite having congenital ocular malformations, infants infected prenatally with the Zika virus (ZIKV) appear to undergo normal eye development after birth, results of a study in primates indicate.1
Fetal and neonatal birth defects associated with ZIKV include retinal colobomas and other ocular anomalies, microcephaly, musculoskeletal contractures, and neurological deficits. Some prenatally infected babies are born without microcephaly but with eye defects, noted study coauthor Glenn Chung-Wing Yiu, MD, PhD, at the University of California, Davis.
“Before our study,” Dr. Yiu said, “it was unclear if the virus continues to replicate or affect eye development after birth.”
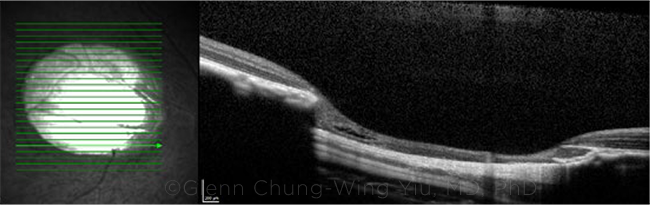 |
COLOBOMA. Near infrared and optical coherence tomography images of a chorioretinal coloboma in an infant rhesus monkey that was infected with ZIKV in utero.
|
Study specifics. Dr. Yiu and his colleagues infected six pregnant rhesus monkeys with ZIKV during their first trimester. Early fetal loss or stillbirth occurred in four monkeys, but the other two gave birth to infants whose eye development was monitored for two years.
Outcomes. Neither infant had neurological or behavioral defects, and there was no indication of continued viral replication after birth, the researchers found.
Both eyes of one monkey showed large retinal colobomas, as well as thinning of photoreceptor and retinal ganglion cell layers as compared with normal infant monkeys, Dr. Yiu said. Despite the colobomas, the eyes showed normal axial elongation and development of retinal layers as the infant grew, he said.
Pre- versus postnatal. The findings indicate that the ocular impacts of ZIKV infection occur primarily in utero, with no sign of active ZIKV replication after birth, Dr. Yiu said. “This should be reassuring to ophthalmologists following children with this condition.”
—Linda Roach
___________________________
1 Yiu G et al. JCI Insight. 2020;5(24):143947.
___________________________
Relevant financial disclosures—Dr. Yiu: None.
For full disclosures and the disclosure key, see below.
Full Financial Disclosures
Dr. Antoszyk Genentech: C,S; Jaeb Center for Health Research: C; Novartis: C; Opthea: C; Regeneron: C; Roche: C,S.
Dr. Fekrat None.
Dr. Grewal None.
Dr. Nath None.
Dr. Yiu Alimera: C; Allergan: C; Carl Zeiss: C; Clearside Biomedical: C,S; Genentech: C,S; Iridex: C,S; Intergalactic Therapeutics: C; Topcon: C; Verily: C.
Disclosure Category
|
Code
|
Description
|
| Consultant/Advisor |
C |
Consultant fee, paid advisory boards, or fees for attending a meeting. |
| Employee |
E |
Employed by a commercial company. |
| Speakers bureau |
L |
Lecture fees or honoraria, travel fees or reimbursements when speaking at the invitation of a commercial company. |
| Equity owner |
O |
Equity ownership/stock options in publicly or privately traded firms, excluding mutual funds. |
| Patents/Royalty |
P |
Patents and/or royalties for intellectual property. |
| Grant support |
S |
Grant support or other financial support to the investigator from all sources, including research support from government agencies (e.g., NIH), foundations, device manufacturers, and/or pharmaceutical companies. |
|
More from this month’s News in Review