Download PDF
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and the more severe variant, toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), are dermatologic immune-mediated emergencies with serious ophthalmic consequences, including corneal perforation and blindness. First and foremost, it is critical to recognize these entities early, as they can progress rapidly to an acute and life-threatening disorder. Most frequently triggered by a medication, SJS/TEN can also be elicited by the host’s response to an infectious organism.
These disorders are characterized by a macular rash, bullous lesions, epidermal sloughing, and necrosis of the skin and mucous membranes.1 In the majority of cases, there is ocular surface involvement. A thorough ophthalmic examination is always warranted.2,3
The distinction between SJS and TEN is based on the percentage of total body surface area (BSA) affected:
- SJS = less than 10% of BSA
- SJS/TEN overlap = 10% to 30% of BSA
- TEN = more than 30% of BSA
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
SJS/TEN is a rare disorder, affecting 0.4 to 7 patients per 1 million population. The mortality rate in SJS is between 1% and 5% and is significantly higher in the TEN variant, at 25% to 40%.3 Of note, the risk of developing SJS/TEN is up to 100 times greater in HIV-infected persons.4 Other risk factors include active malignancy, systemic lupus erythematous, certain genetic polymorphisms, and various human leukocyte antigen (HLA) haplotypes.3 TEN is 2.7 times more likely in elderly patients, and mortality is twice as high in this group.4
Presentation and Diagnosis
Frequently presenting with a prodromal flu-like illness of approximately three days’ duration, SJS/TEN progresses to a painful rash that spreads and blisters. Skin involvement initially consists of ill-defined erythematous macules with purpuric centers, which rapidly coalesce; alternatively, there may be diffuse generalized erythema before development of bullae and vesicles.1,4
The differential diagnosis for SJS/TEN includes the following entities:
- Erythema multiforme
- Erythematous drug eruption
- Toxic epidermal necrosis–like acute cutaneous lupus
- Linear IgA bullous dermatosis
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
- Paraneoplastic pemphigus
The diagnosis of SJS/TEN is made through clinical assessment and a skin biopsy showing subepidermal blisters with full-thickness necrosis, apoptotic keratinocytes, and minimal involvement of the underlying dermis.1,4 Upon diagnosis, transfer of the patient to a facility with a burn intensive care unit is recommended.1
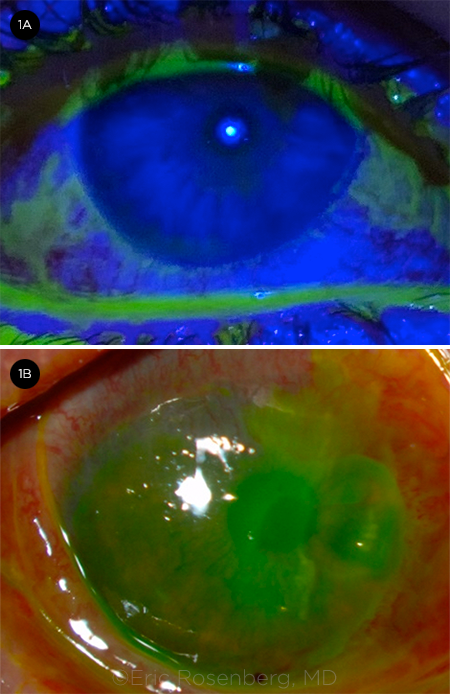
Mucous membranes (ocular, oral, and genital) are almost always affected, and acute ocular involvement is reported to occur in approximately 50% to 88% of cases.3 The entire ocular surface is at risk of involvement, including the bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva, fornices, and cornea. If SJS/TEN is suspected, ophthalmic examination should be performed at the time of diagnosis and thereafter on a daily basis during hospitalization. The entire ocular surface should be examined with fluorescein staining to evaluate for membranes, conjunctival involvement, and epithelial defects (Fig. 1).1
 |
|
ACUTE COMPLICATIONS. (1A) Bulbar and palpebral conjunctival hyperemia with staining and early sloughing of the periocular and surrounding epidermis. (1B) Impending corneal perforation with a large, staining 8-mm epithelial defect.
|
Causes
Hypersensitivity reaction to a drug causes the majority of SJS/TEN cases. Over 200 medications have been linked to the pathology, but the most common offenders include sulfonamide antibiotics, anticonvulsants, allopurinol, beta-lactam antibiotics, nevirapine, abacavir, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, lamotrigine, and chlormezanone.1,4 The remaining minority of cases are caused by infections, of which Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the most common infectious agent.2 Herpes simplex virus infection is a rare cause and is more often associated with erythema multiforme.1
Mechanism
SJS/TEN is primarily categorized as a delayed-type (type IV) hypersensitivity reaction. Keratinocytes process the inciting molecules and present them on major histocompatibility class I complexes to cytotoxic T-cells, resulting in T-cell proliferation, T-cell recruitment, and natural killer cell recruitment. Activated lymphocytes in turn mediate cell death via Fas/FasL, perforin/granzyme B, granulysin, and cytokine mechanisms.1 Granulysin is a key mediator of keratinocyte apoptosis and is found at serum levels of two to four times normal in the early stages of SJS/TEN.4
Various HLA haplotypes have been implicated in the pathogenesis of SJS/TEN. The HLA-A*02:06 and HLA-B*44:03 haplotypes have been shown to increase the risk of developing severe ocular complications.5 In addition, genetic risk factors such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the TLR3 and EP3 genes have been shown to be highly associated with the development of SJS within the Japanese population.1,5
Acute Ocular Complications
The acute phase of SJS lasts for eight to 12 days. It is followed by two to four weeks of re-epithelialization of denuded skin. Acute phase ophthalmic manifestations vary widely and include conjunctival hyperemia, subconjunctival hemorrhage, conjunctival pseudomembranes, true membranes, symblepharon formation, forniceal shortening, epithelial defects, corneal ulceration, meibomitis, and eyelid margin ulceration. These complications ultimately contribute to limbal stem cell dysfunction (LSCD), which may play a role in the chronic ocular complications discussed below.3
Acute phase management. During the acute phase, it is judicious to perform daily ophthalmic exams, with closer follow-up intervals depending on the extent of ocular involvement. See the table for grading and treatment of ocular involvement in acute SJS/TEN.
Amniotic membrane. Amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) using a symblepharon ring has been shown to improve ophthalmic outcomes and should be performed within the first few days of the onset of symptoms in patients with severe or extremely severe involvement.3,6,7 Methods for securing the amniotic membrane include sutured and self-retaining techniques.
The first-reported use of AMT for SJS/TEN employed a sutured technique. Benefits of this method include a well-placed amniotic membrane that covers all ocular surface structures including the eyelid margin; however, limitations include a lengthy surgical process; placement of sutures in friable skin; and, frequently, the need for general anesthesia, which may be contraindicated in a critically ill patient.
Alternatively, there are two sutureless options, obviating the need for general anesthesia. First, the self-retaining ProKera (BioTissue) corneal bandage device consists of amniotic membrane affixed to a ring that is worn as a contact lens. However, this device covers only the cornea and perilimbal conjunctiva and, thus, is not effective for patients with involvement of the eyelid margin and palpebral conjunctiva.
Second, in lieu of sutures, cyanoacrylate glue may be used to fasten the amniotic membrane in place; this technique can be used to provide coverage for the entire ocular surface. There is no evidence that there is a difference in long-term outcomes between sutured and sutureless AMT techniques.8
The exact mechanism by which AMT exerts a beneficial effect is not yet fully elucidated. However, it is known that amniotic membrane has antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties and that it promotes epithelialization. In addition, AMT has low immunogenicity.3,6
Systemic treatment. Systemic therapies for SJS/TEN are a subject of continued debate. To date, systemic corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin have been studied for their effects on ocular disease. Currently, there is no clear evidence for the effectiveness of either modality in treating the ocular manifestations of SJS/TEN.3,6
Chronic Ocular Complications
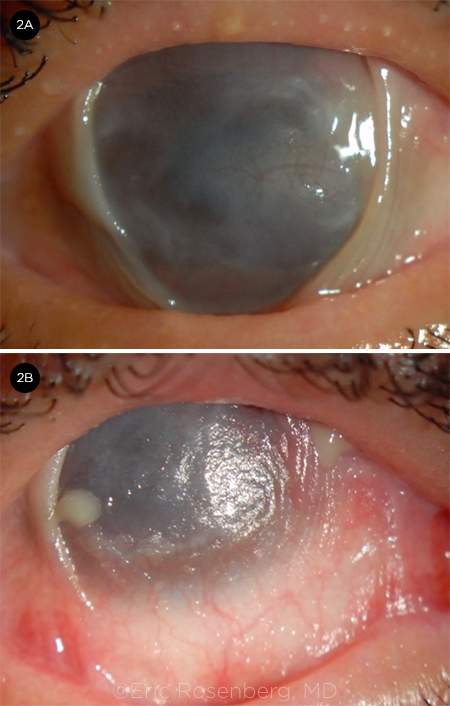
Roughly 30% to 50% of SJS/TEN patients go on to develop chronic ocular complications (Fig. 2).6 These complications include trichiasis, eyelid malposition, posterior eyelid margin and surface keratinization, symblepharon formation, severe dry eye, persistent corneal epithelial defects, corneal neovascularization, LSCD, and end-stage corneal blindness.3
Chronic phase management. In chronic SJS, the ocular surface is compromised, and treatment revolves around preventing progressive ocular surface damage.3 The type and schedule of ophthalmic follow-up and examination are highly dependent on ocular presentation.
Frequently observed chronic ocular complications are the loss of limbal stem cells and abnormal meibomian glands. Further, it is common to encounter eyelid disorders, trichiasis, and symblepharon formation, which can be treated with entropion repair, epilation, and cicatricial release, respectively. Topical retinoic acid to the eyelid margin has also been shown to aid in the reduction of keratinization.
If these measures fail, scleral contact lenses and autologous oral mucous membrane grafting may be employed. End-stage corneal blindness may necessitate a keratoprosthesis device, as the failure rate of penetrating keratoplasty is significantly higher in SJS/TEN than in other conditions.
Presently available keratoprosthesis options include the Boston keratoprosthesis (BKP) types I and II and the modified osteo-odonto keratoprosthesis (MOOKP).
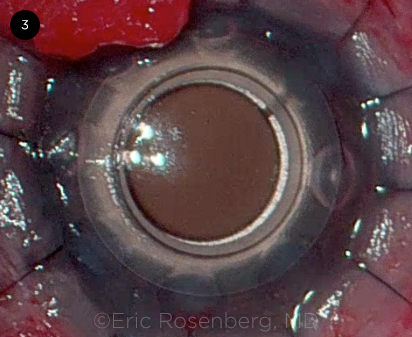
BKP types I and II are collar button–shaped devices with an optical stem. BKP type I is appropriate for patients with nonxerotic eyes with normal eye-lid function. Eyes with poor lid function and poor ocular surfaces may require either the BKP type II or MOOKP; however, these surgeries are generally performed only by a few subspecialists worldwide (Fig. 3).3,7 The most common complications of BKP type I and II are retroprosthetic membrane, glaucoma, and infectious endophthalmitis.2
 |
|
CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS. (2A) Corneal opacification from limbal stem cell deficiency with nasal and temporal symblepharon formation. (2B) Xerotic, neovascularized, and keratinized cornea with severe symblepharon and cicatricial lid changes.
|
 |
|
KERATOPROSTHESIS. (3) Intraoperative photograph of the placement of a BKP type I in a patient with a history of SJS/TEN. Note the transparent central PMMA optic, donor cornea sandwiched between the front and perforated rear plate, and the 12 interrupted nylon sutures.
|
Outcomes
Mild acute ocular involvement that is not treated can progress to severe long-term complications.2,3 Although the severity of skin manifestations may not correlate directly with ocular outcomes, it has been demonstrated that patients who receive timely medical and/ or surgical treatment generally have improved ocular outcomes.3,6
Prompt AMT in the severe acute phase, and early medical intervention in the milder stages, have been shown to improve long-term outcomes.2,6 Not surprisingly, patients with very severe ocular disease experience more complications, with many requiring multiple AMTs due to persistent inflammation. These patients are also more likely to have scarring, dry eye, and photophobia.6
Grading and Treatment of Ocular Manifestations of Acute SJS/TEN
| Grade |
Ocular Involvement |
Treatment |
| Mild |
No ocular involvement |
Artificial tears, 4 times/day to every 2 hours; artificial tear ointment at bedtime |
| Moderate |
Stain <1/3 of lid margin length; no corneal staining (or, at most, staining of punctate epithelial erosions); <1 cm of conjunctival staining |
Moxifloxacin 0.5%, 4 times/day; prednisone 1%, 4 times/day to every 4 hours; fluorometholone 0.1% ointment, 4 times/day; artificial tears, every hour; artificial tear ointment, every 4 hours |
| Severe |
Stain >1/3 of lid margin length; any corneal epithelial defects (except for punctate epithelial erosion); >1 cm of conjunctival staining |
Therapies above, plus amniotic membrane transplantation* |
| Extremely severe |
Complications above, plus multiple areas of conjunctival staining >1 cm |
Therapies above, plus urgent amniotic membrane transplantation* |
*If patient is obtunded, consider additional modalities to protect the ocular surface including moisture chambers.
SOURCE: Adapted from Gregory DG. Ophthalmology. 2016;123(8):1653-1658. |
Conclusion
SJS/TEN is a severe, potentially blinding immune-mediated dermatobullous disorder that affects both the skin and eyes. It is usually caused by a drug hypersensitivity reaction and has strong HLA associations. Upon diagnosis, an ophthalmologist should promptly evaluate the patient’s ocular surface and initiate care. Unaddressed, even mild disease may progress to end-stage blindness, and appropriate, timely acute-stage treatment is the best preventive against chronic sequelae. Medical treatment is appropriate for mild and moderate disease; however, AMT should be considered and performed in cases of severe and extremely severe disease.
__________________________
1 Kohanim S et al. Ocul Surf. 2016;14(1):2-19.
2 Jain R et al. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016;61(4):269-399.
3 Kohanim S et al. Ocul Surf. 2016;14(2):168-188.
4 Lerch M et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54(1):147-176.
5 Ueta M. Cornea. 2015;34(Suppl 11):S158-S165.
6 Gregory DG. Ophthalmology. 2016;123(8):1653-1658.
7 Saeed HN, Chodosh J. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2016;27(6):522-529.
8 Shanbhag SS et al. Ocul Surf. 2019;17(3):560-564.
Mr. Thuma is a medical student at Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, New York, N.Y. Dr. Rosenberg is a cornea, refractive, and complex anterior segment surgeon at SightMD in Babylon, N.Y. Financial disclosures: None.