A hyphema is when blood collects inside the front of the eye. This happens between the cornea (the clear, dome-shaped window at the front of the eye) and the iris (the colored part of the eye). The blood may cover part or all of the iris and the pupil (the round, dark circle in the middle of your eye). If you have a hyphema, your vision might be partly or totally blocked in that eye.
A hyphema usually happens when an injury causes a tear of the iris or pupil of the eye. Sometimes people mistake a broken blood vessel in the front of the eye for a hyphema. A broken blood vessel in the eye is a common, harmless condition called subconjunctival hemorrhage. A subconjunctival hemorrhage does not hurt. A hyphema, though, is usually painful. A hyphema must be treated properly or it can cause permanent vision problems.
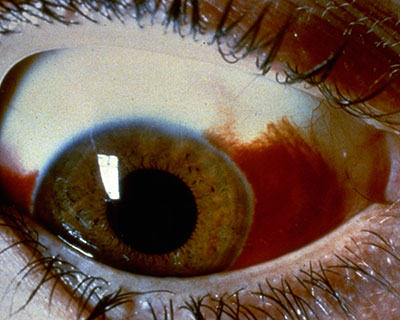
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is when blood appears in the white of the eye from a broken blood vessel.
Hyphema Symptoms
Hyphema symptoms include:
- bleeding in the front of the eye
- sensitivity to light
- pain in the eye
- blurry, clouded or blocked vision
Hyphema Causes
Hyphema is usually caused by injuries to the eye from accidents or playing sports. Hyphema can be caused by other, less common things, including:

Always wear the right eye protection when playing sports.
Because most hyphemas happen because of sports injuries, it is important to wear protective eyewear. Sports injuries, especially with small balls like racquetballs, can cause serious eye problems. Besides hyphema, these injuries can cause cataracts, retinal detachments and glaucoma and lead to blindness. If you hurt your eye, see an ophthalmologist right away.
How Is Hyphema Diagnosed?
An ophthalmologist will examine your eye completely to diagnose a hyphema. They will check:
In some cases, the ophthalmologist may order a CT scan. This scan checks the condition of the bones that form your eye sockets and other parts of your face.
How Is Hyphema Treated?
Based on what the ophthalmologist finds when examining your hyphema, they may ask you to:
- wear a special shield over your eye to protect it
- cut back on physical activity, or to rest in bed
- raise the head of your bed to help your eye drain
- see your ophthalmologist often so they can check your healing and eye pressure. They may prescribe eye drops to decrease the swelling inside your eye and to ease the pain or discomfort.
Your ophthalmologist may tell you not to use aspirin because it can lead to more bleeding. In some cases, your ophthalmologist might tell you to go to the hospital so that your eye can be cared for and checked often. If the hyphema makes your eye pressure rise too high, it can lead to glaucoma or damage your cornea. If this happens, you may need surgery to remove the excess blood or eye drops for treatment.