Download PDF
Researchers have conducted a validation study of the recently published AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, eighth edition (AJCC 8) and have found significant changes in definitions of tumor (T) and lymph node (N) categories. Whereas the T category definitions in AJCC 7 included perineural invasion and subjective terms, these criteria were removed in AJCC 8.
“T category distribution in AJCC 7 differed significantly from T category distribution in AJCC 8,” said lead investigator Bita Esmaeli, MD, at MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“In our study, we found that AJCC 8 allows for a more precise designation of T category and a more homogeneous distribution of eyelid squamous cell carcinomas across the T categories.”1
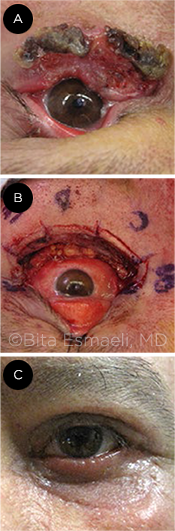 |
SQUAMOUS CELL. This patient’s lesion was at least a T2c (A). The margins were clear on frozen section (B). The immediate reconstructive outcome after a tarsoconjunctival flap and a full-thickness skin graft (C).
|
Comparison of classifications. In this single-center cohort study of 109 patients with eyelid and periocular squamous cell carcinoma, T category differed in 33 patients.
Twenty patients with T3 disease per AJCC 7 had T4 disease per AJCC 8. Local recurrence-free survival seemed better for patients with T4 than for those with T3 tumors, and the proportion of patients with local recurrence was higher among those with T3 tumors. Similarly, six patients with histologic perineural invasion, classified as T3a disease in AJCC 7, had T2a or T2b disease when classified by AJCC 8.
Main outcomes and measures. Main outcomes measured in this study were local recurrence, nodal metastasis (NM), distant metastasis, and disease-specific survival (DSS).
Forty-three patients presented with recurrent eyelid or periocular squamous cell carcinoma, and 11 patients developed local recurrence during follow-up. NM was significantly associated with T category at presentation and was more common in patients with T2c, T3a, and T3b or more advanced tumors. NM at presentation and follow-up was associated with increased risk of distant metastasis. For patients with T4 disease, the two-year DSS rate was 92.6% and the five-year DSS rate was 87.7%. DSS was significantly worse in patients with T2c, T3a, and T3b or more advanced tumors. T4 disease was associated with worse DSS, but NM at presentation was not.
Limitations. This study was retrospective, and the univariate factors could be associated with one another. Due to the small number of events in each category, a multivariate analysis was not possible.
Conclusions. The bottom line: AJCC 8 shows better predictive value in terms of local recurrence and DSS. Immunosuppression and presentation with recurrent disease are associated with increased risk of future local recurrence.
Patients with tumors of clinical stage of T2c or worse at presentation in the AJCC 8 are at higher risk of NM and worse DSS and should undergo surveillance for NM, the authors said.
—Arthur Stone
___________________________
1 Xu S et al. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online March 14, 2019.
___________________________
Relevant financial disclosures—Dr. Esmaeli: None.
For full disclosures and the disclosure key, see below.
Full Financial Disclosures
Dr. Esmaeli None.
Dr. Ferdi Northcote Trust: S.
Dr. Rong None.
Dr. Tam None.
Disclosure Category
|
Code
|
Description
|
| Consultant/Advisor |
C |
Consultant fee, paid advisory boards, or fees for attending a meeting. |
| Employee |
E |
Employed by a commercial company. |
| Speakers bureau |
L |
Lecture fees or honoraria, travel fees or reimbursements when speaking at the invitation of a commercial company. |
| Equity owner |
O |
Equity ownership/stock options in publicly or privately traded firms, excluding mutual funds. |
| Patents/Royalty |
P |
Patents and/or royalties for intellectual property. |
| Grant support |
S |
Grant support or other financial support to the investigator from all sources, including research support from government agencies (e.g., NIH), foundations, device manufacturers, and/or pharmaceutical companies. |
|
More from this month’s News in Review